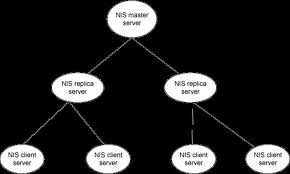
 NIS SERVER CONFIGURATION (NETWORK INFORMATION SERVICE)
SERVER CONFIGURATION
Note:
NIS SERVER CONFIGURATION (NETWORK INFORMATION SERVICE)
SERVER CONFIGURATION
Note: While NIS configuring time disable the firewall/iptables service (service iptables stop), later will configure firewall setting with NIS server.
Requirement:
1. Portmap (Default Installed)
2. Yp-tools (Default Installed)
3. Ypbind (Need To Install)
4. Ypserv (Need To Install)
Install Required Packages/tools:
[root@sandeep~]# rpm -i ypserv-2.13-5.x86_64.rpm (Install ypserv package)
[root@sandeep~]# rpm -i ypbind-1.17.2-3.x86_64.rpm (Install ypbind package)
Check Required Packages are Installed On NIS Server:
[root@sandeep ~]# rpm -qa portmap
portmap-4.0-63
[root@sandeep ~]# rpm -qa yp-tools
yp-tools-2.8-7
[root@sandeep ~]# rpm -qa ypbind
ypbind-1.17.2-3
[root@sandeep ~]# rpm -qa ypserv
ypserv-2.13-5
[root@sandeep ~]#
Edit Your /etc/sysconfig/network File
(You need to add the NIS domain you wish to use in the /etc/sysconfig/network file. For the SANDEEP, call the domain SANDEEP-NIS-SERVER.)
[root@sandeep ~]# vi /etc/sysconfig/network
NETWORKING=yes
HOSTNAME=sandeep
NISDOMAIN=
"SANDEEP-NIS-SERVER"
Edit Your /etc/yp.conf File
[root@sandeep ~]# vi /etc/yp.conf
# ypserver 192.168.1.11
Start the Key NIS server related daemons
Start the necessary NIS daemons in the /etc/init.d directory and use the chkconfig command to ensure they start after the next reboot
[root@sandeep]# service portmap start
Starting portmapper: [ OK ]
[root@sandeep]# service yppasswdd start
Starting YP passwd service: [ OK ]
[root@sandeep]# service ypserv start
Setting NIS domain name SANDEEP-NIS-SERVER: [ OK ]
Starting YP server services: [ OK ]
[root@sandeep]#
[root@sandeep]# chkconfig portmap on
[root@sandeep]# chkconfig yppasswdd on
[root@sandeep]# chkconfig ypserv on
[root@sandeep ~]# rpcinfo -p localhost
program vers proto port
100000 2 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 2 udp 111 portmapper
100024 1 udp 32769 status
100024 1 tcp 32769 status
100004 2 udp 862 ypserv
100004 1 udp 862 ypserv
100004 2 tcp 865 ypserv
100004 1 tcp 865 ypserv
600100069 1 udp 872 fypxfrd
600100069 1 tcp 874 fypxfrd
100009 1 udp 715 yppasswdd
Initialize Your NIS domain (Add Clients on NIS network)
[root@sandeep ~]# /usr/lib64/yp/ypinit -m
At this point, we have to construct a list of the hosts which will run NIS
servers. sandeep is in the list of NIS server hosts. Please continue to add
the names for the other hosts, one per line. When you are done with the
list, type a
.
next host to add: sandeep
next host to add: sandeep1
next host to add: sandeep2
next host to add:
(Press Y and)
The current list of NIS servers looks like this:
sandeep
sandeep1
sandeep2
Is this correct? [y/n: y] y
We need a few minutes to build the databases...
Building /var/yp/SANDEEP-NIS-SERVER/ypservers...
gethostbyname(): Success
Running /var/yp/Makefile...
gmake[1]: Entering directory `/var/yp/SANDEEP-NIS-SERVER'
Updating passwd.byname...
Updating passwd.byuid...
Updating group.byname...
Updating group.bygid...
Updating hosts.byname...
Updating hosts.byaddr...
Updating rpc.byname...
Updating rpc.bynumber...
Updating services.byname...
Updating services.byservicename...
Updating netid.byname...
Updating protocols.bynumber...
Updating protocols.byname...
Updating mail.aliases...
gmake[1]: Leaving directory `/var/yp/SANDEEP-NIS-SERVER'
sandeep has been set up as a NIS master server.
Now you can run ypinit -s sandeep on all slave server.
[root@sandeep ~]#
Start ypbind and ypxfrd Daemons:
[root@sandeep]# service ypbind start
Binding to the NIS domain: [ OK ]
Listening for an NIS domain server.
[root@sandeep]# service ypxfrd start
Starting YP map server: [ OK ]
[root@sandeep]# chkconfig ypbind on
[root@sandeep]# chkconfig ypxfrd on
Make sure daemons are running fine.
[root@sandeep ~]# rpcinfo -p localhost
program vers proto port
100000 2 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 2 udp 111 portmapper
100024 1 udp 32769 status
100024 1 tcp 32769 status
100004 2 udp 862 ypserv
100004 1 udp 862 ypserv
100004 2 tcp 865 ypserv
100004 1 tcp 865 ypserv
600100069 1 udp 872 fypxfrd
600100069 1 tcp 874 fypxfrd
100009 1 udp 715 yppasswdd
[root@sandeep ~]#
Adding New NIS Users
[root@sandeep]# useradd -g users nisuser
[root@sandeep]# passwd nisuser
Changing password for user nisuser.
New password:
Retype new password:
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
[root@sandeep]# cd /var/yp
[root@sandeep yp]# make
gmake[1]: Entering directory `/var/yp/NIS-SCHOOL-NETWORK'
Updating passwd.byname...
Updating passwd.byuid...
Updating netid.byname...
gmake[1]: Leaving directory `/var/yp/NIS-SCHOOL-NETWORK'
[root@sandeep yp]#
You can check to see if the user's authentication information has been updated by using the ypmatch command, which should return the user's encrypted password string.
[root@sandeep yp]# ypmatch nisuser passwd
nisuser:$1$d6E2i79Q$wp3Eo0Qw9nFD/::504:100::/home/nisuser:/bin/bash
[root@sandeep yp]
You can also use the getent command, which has similar syntax. Unlike ypmatch, getent doesn't provide an encrypted password when run on an NIS server, it just provides the user's entry in the /etc/passwd file. On a NIS client, the results are identical with both showing the encrypted password.
[root@sandeep yp]# getent passwd nisuser
nisuser:x:504:100::/home/nisuser:/bin/bash
[root@sandeep yp]#
FIREWALL CONFIGURATION WITH NIS SERVER:
Edit /etc/sysconfig/iptables file for Enabling NIS (ypbind/portmap port – 111), Enable port no 111 for TCP as well as UDP. (Two lines given bellow just add in iptables file and save & exit)
[root@sandeep ~]# cd /etc/sysconfig/
[root@sandeep sysconfig]# vi iptables
-A RH-Firewall-1-INPUT -p tcp -m state --state NEW -m tcp --dport 111 -j ACCEPT
-A RH-Firewall-1-INPUT -p udp -m udp --dport 111 -j ACCEPT
:wq Enter (Save iptables file and exit)
Restart iptables service:
(Check service should not be [Fail],everything should be [OK])
[root@sandeep ~]# service iptables restart
Flushing firewall rules: [ OK ]
Setting chains to policy ACCEPT: filter [ OK ]
Unloading iptables modules: [ OK ]
Applying iptables firewall rules: [ OK ]
[root@sandeep ~]#
Restart ypbind service:
(Once restart ypbind service, check whether it will restart or not after enabling 111 port & starting firewall)
[root@sandeep ~]# service ypbind restart
Shutting down NIS services: [ OK ]
Binding to the NIS domain: [ OK ]
Listening for an NIS domain server.
[root@sandeep ~]#
CLIENT CONFIGURATION:
Note: While NIS Client configuring time disable the firewall/iptables service (service iptables stop), later will configure firewall setting with NIS server.
Run authconfig
The authconfig or the authconfig-tui program automatically configures your NIS files after prompting you for the IP address and domain of the NIS server
[root@sandeep2 ~]# authconfig-tui
Once finished, it should create an /etc/yp.conf file that defines, amongst other things, the IP address of the NIS server for a particular domain. It also edits the /etc/sysconfig/network file to define the NIS domain to which the NIS client belongs.
Requirement Of Package for Client Machine:
1. Portmap
2. Yp-tools
3. Ypbind
[root@sandeep2 etc]# vi yp.conf
domain SANDEEP-NIS-SERVER server 192.168.1.11
[root@sandeep2 etc]# vi /etc/sysconfig/network
NETWORKING=yes
HOSTNAME=sandeep2
NISDOMAIN=SANDEEP-NIS-SERVER
[root@sandeep2 etc]# cat nsswitch.conf
passwd: files nis
shadow: files nis
group: files nis
Start The NIS Client Related Daemons
[root@sandeep2 etc]# service portmap start
Starting portmap: [ OK ]
[root@sandeep2 etc]# service ypbind start
Binding to the NIS domain: [ OK ]
Listening for an NIS domain server.
[root@sandeep2 etc]# chkconfig ypbind on
[root@sandeep2 etc]# chkconfig portmap on
[root@sandeep2 etc]#
Note:
Remember to use the rpcinfo -p localhost command to make sure they all started correctly.
[root@sandeep2 etc]# rpcinfo -p
program vers proto port
100000 2 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 2 udp 111 portmapper
100024 1 udp 32768 status
100024 1 tcp 32769 status
100011 1 udp 931 rquotad
100011 2 udp 931 rquotad
100011 1 tcp 934 rquotad
100011 2 tcp 934 rquotad
100003 2 udp 2049 nfs
100003 3 udp 2049 nfs
100003 4 udp 2049 nfs
100003 2 tcp 2049 nfs
100003 3 tcp 2049 nfs
100003 4 tcp 2049 nfs
100021 1 udp 32770 nlockmgr
100021 3 udp 32770 nlockmgr
100021 4 udp 32770 nlockmgr
100021 1 tcp 32803 nlockmgr
100021 3 tcp 32803 nlockmgr
100021 4 tcp 32803 nlockmgr
100005 1 udp 952 mountd
100005 1 tcp 955 mountd
100005 2 udp 952 mountd
100005 2 tcp 955 mountd
100005 3 udp 952 mountd
100005 3 tcp 955 mountd
100007 2 udp 1020 ypbind
100007 1 udp 1020 ypbind
100007 2 tcp 1023 ypbind
100007 1 tcp 1023 ypbind
Verify Name Resolution
As the configuration examples refer to the NIS client and server by their hostnames, you'll have to make sure the names resolve correctly to IP addresses. This can be configured either in DNS, when the hosts reside in the same domain, or more simply by editing the /etc/hosts file on both Linux boxes.
[root@sandeep2 etc]# vi hosts [Enter server IP and Machine Name]
# Do not remove the following line, or various programs
# that require network functionality will fail.
192.168.1.9 sandeep1 sandeep1
192.168.1.10 sandeep2 sandeep2 192.168.1.10
192.168.1.11 sandeep sandeep
127.0.0.1 localhost.localdomain localhost
[root@sandeep2 etc]#
Test NIS Access To The NIS Server
[root@sandeep2 etc]# ypcat passwd
nisuser:$1$6x8OLUK/$hzSCrGreGmaLie4.bJhmZ/:509:100::/home/nisuser:/bin/bash
sandeep:$1$uYwOkipg$h9lz.9mf896yKl.uDZeOy/:513:513::/home/sandeep:/bin/bash
ftp1:$1$b/0QI9C.$NgdU6DmNXN.X5r3vHIQhf0:510:515::/home/ftp1:/bin/bash
general:$1$wi.oLbwp$QRQaqFCWi8SRoxO674gyg/:511:511::/home/general:/bin/bash
tech:$1$xEBawVW.$LLATEJY0lOrWWbOpId3TL1:512:512::/home/tech:/bin/bash
[root@sandeep2 etc]#
[root@sandeep2 etc]# ypmatch nisuser passwd
nisuser:$1$6x8OLUK/$hzSCrGreGmaLie4.bJhmZ/:509:100::/home/nisuser:/bin/bash
[root@sandeep2 etc]#
[root@sandeep2 etc]# getent passwd nisuser
nisuser:$1$6x8OLUK/$hzSCrGreGmaLie4.bJhmZ/:509:100::/home/nisuser:/bin/bash
[root@sandeep2 etc]#
Test Logins via The NIS Server
Logging In Via SSH
Click On SSH Secure Shell → Quick Connect → Host Name (Give Client IP Address) 192.168.1.10 → User Name (Give Created nisuser in server) nisuser → Connect → Password (nisuser123) → you will get bash screen [Last login: Wed Feb 10 12:59:46 2010 from 192.168.1.212
-bash-3.00$
]
FIREWALL CONFIGURATION WITH NIS CLIENT:
Edit /etc/sysconfig/iptables file for Enabling NIS (ypbind/portmap port – 111), Enable port no 111 for TCP as well as UDP. (Two lines given bellow just add in iptables file and save & exit)
[root@sandeep2 ~]# cd /etc/sysconfig/
[root@sandeep2 sysconfig]# vi iptables
-A RH-Firewall-1-INPUT -p tcp -m state --state NEW -m tcp --dport 111 -j ACCEPT
-A RH-Firewall-1-INPUT -p udp -m udp --dport 111 -j ACCEPT
:wq Enter (Save iptables file and exit)
Restart iptables service:
(Check service should not be [Fail],everything should be [OK])
[root@sandeep2 ~]# service iptables restart
Flushing firewall rules: [ OK ]
Setting chains to policy ACCEPT: filter [ OK ]
Unloading iptables modules: [ OK ]
Applying iptables firewall rules: [ OK ]
[root@sandeep2 ~]#
Restart ypbind service:
(Once restart ypbind service, check whether it will restart or not after enabling 111 port & starting firewall)
[root@sandeep2 ~]# service ypbind restart
Shutting down NIS services: [ OK ]
Binding to the NIS domain: [ OK ]
Listening for an NIS domain server.
[root@sandeep2 ~]#
Troubleshoot with NIS server & Client:
Note: If firewall is running in Server then client ypbind will not start, so 1st take care of firewall, stop firewall and restart ypbind in server, then restart firewall & ypbind in client machine then restart firewall in server, then you wont get any kind of error. [if you have started firewall in server machine then trying to start ypbind with firewall in client side you wont get OK result, you will be get only Fail result after long time so keep in mind that 1st restart ypbind in server → restart firewall & ypbind in client machine → then restart firewall in server]